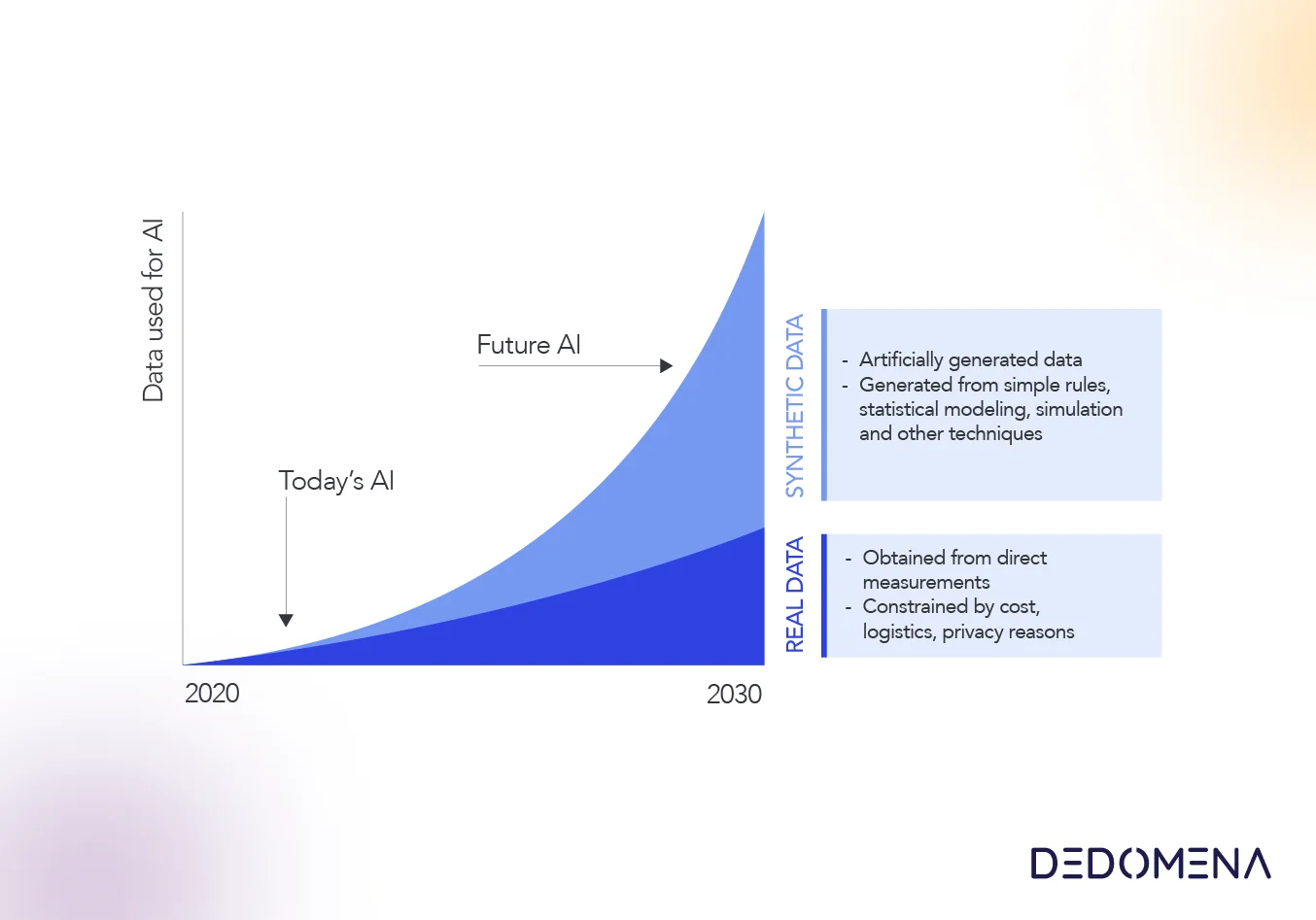
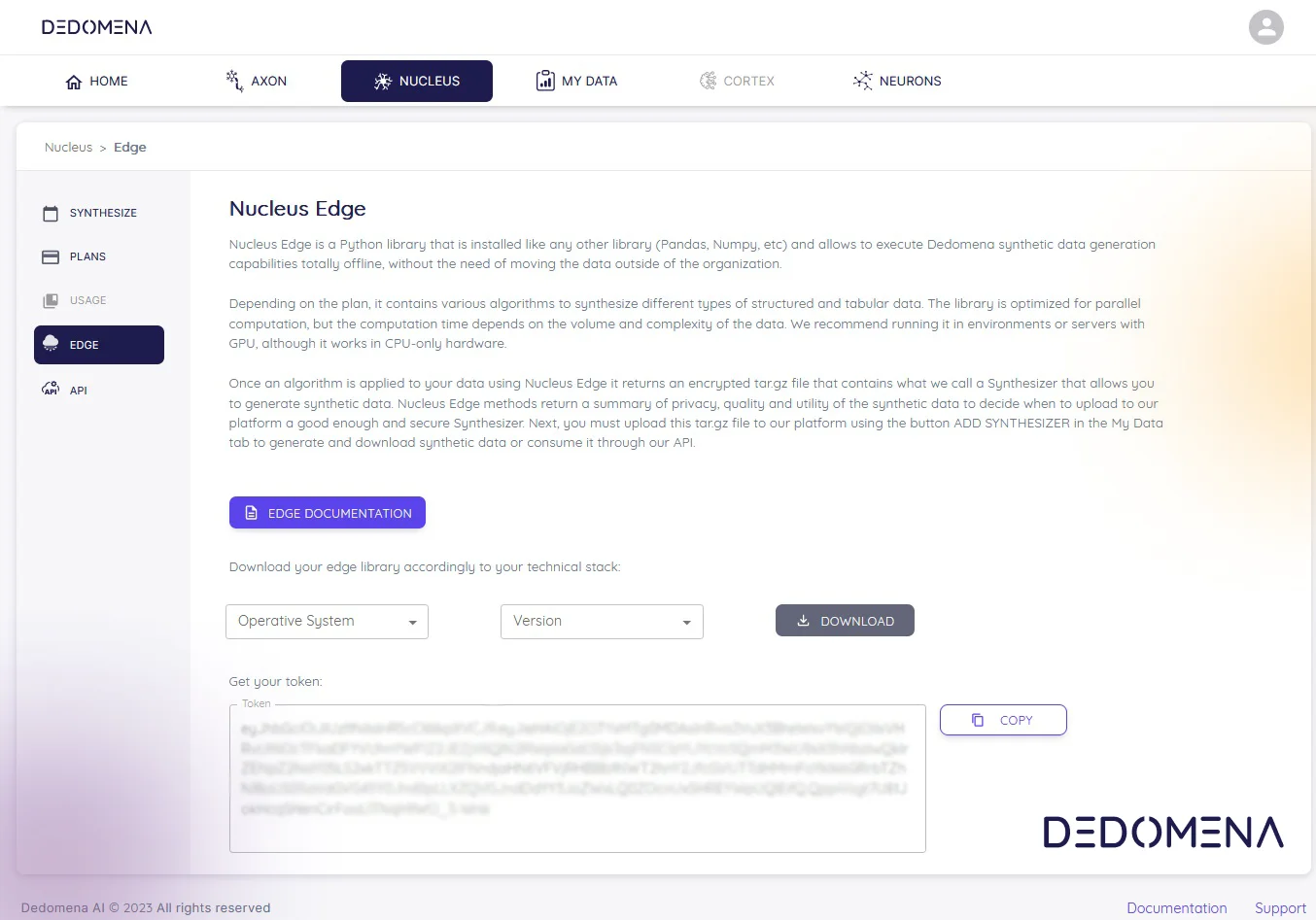
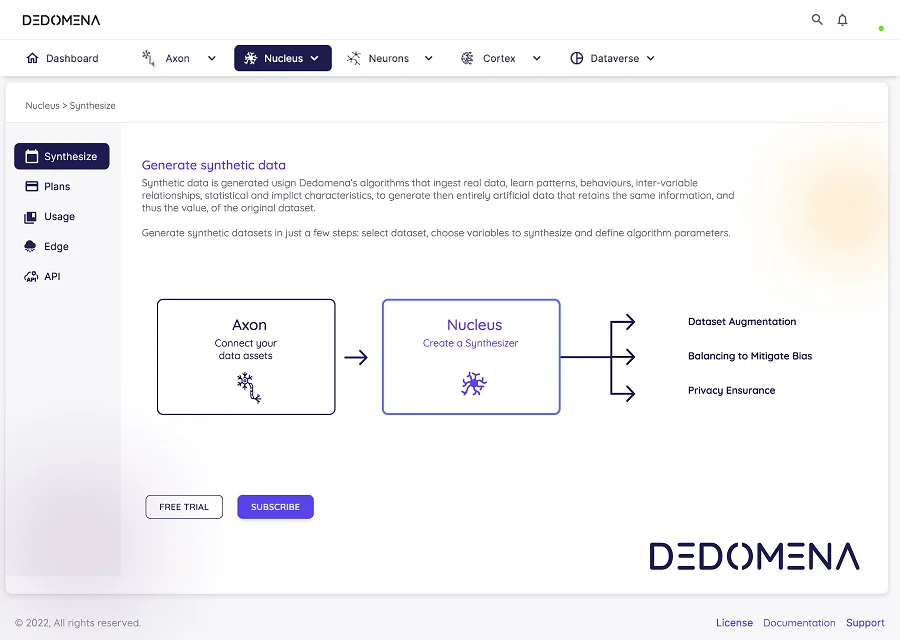
In today's data-driven landscape, safeguarding data privacy is paramount. Enter synthetic data – a revolutionary solution that successfully marries data utility with privacy preservation. In this comprehensive article, we'll take a deep dive into the dynamic world of synthetic data. We'll explore its various types and provide you with real-life examples from diverse industries, highlighting its versatility and transformative potential.
Synthetic data is a sophisticated solution, generated through algorithms to simulate real data while upholding privacy. The demand for synthetic data stems from several compelling reasons:
-
Data Scarcity: Insufficient data often hinders analytics and decision-making, especially for startups.
-
Data Privacy Regulations: Stringent laws like GDPR limit data use, making some data off-limits.
-
Data Security: Sensitive data requires the utmost security, limiting its use.
-
Resource Constraints: Acquiring specific datasets can be costly and complex, posing economic challenges for some organizations.
Types of synthetic data
Our journey into the world of synthetic data covers a spectrum of data types, including text, images, video, audio, and tabular data. These synthetic data formats effectively address challenges related to data privacy, scarcity, and machine learning model training.
-
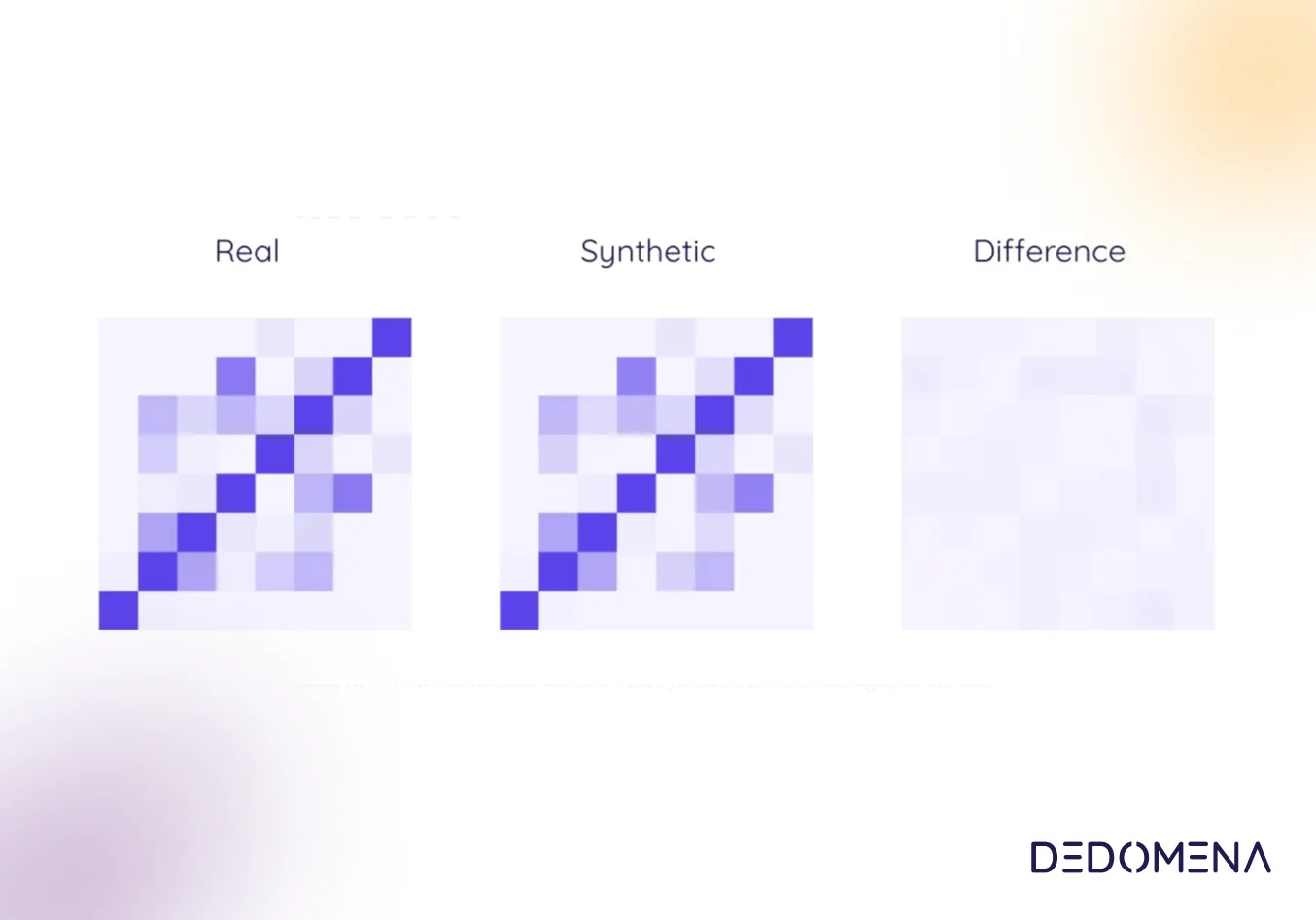
Synthetic Tabular Data: Tabular synthetic data replicates structured data commonly found in databases, such as customer records, transaction logs, and analytical behavior information. This form of synthetic data enables secure and insightful data-driven decision-making.
-
Synthetic Text: Synthetic text comprises artificially generated textual content, harnessed through advanced language models. These models, such as GPT-3, have reached a remarkable level of proficiency in generating human-like text.
-
Synthetic Images: Synthetic images are artificially rendered visual content, mimicking real-world images. This technology finds pivotal application in augmenting datasets used for machine learning, particularly in scenarios where real image data is sensitive or scarce.
-
Synthetic Video: Synthetic videos extend the capabilities of synthetic media to the dynamic realm of video content. It allows the creation of lifelike video data for training machine learning models, filling the gaps when actual video data is inaccessible due to privacy concerns.
-
Synthetic Audio: Synthetic audio involves the artificial generation of sound content. It serves a multitude of purposes, including voice assistant training and sound recognition model development.
Real-World Use Cases of Synthetic Data
Now, let's delve into the real-world applications of synthetic data, spotlighting examples from industries that have harnessed its potential to overcome data scarcity, privacy concerns, and drive data-driven innovation:
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Amazon deploys synthetic data to train its AI systems, like Alexa's language understanding. Synthetic text data proves invaluable when genuine data for new languages is in short supply.
-
Autonomous Vehicles: Waymo, an Alphabet subsidiary, leverages synthetic data for training its self-driving cars. This empowers the simulation of diverse driving scenarios, accelerating the development of autonomous vehicle technology.
-
Predictive Analytics: Financial giants like American Express and J.P. Morgan turn to synthetic data for enhancing fraud detection models. It facilitates improved machine learning model performance without exposing sensitive financial information.
-
Insurance Industry: Health insurance leader Anthem collaborates with Google Cloud to create a synthetic health data platform. This enables the training of AI algorithms while preserving patient data privacy.
-
Healthcare and Clinical Research: Pioneers in the pharmaceutical field, including Roche, and innovators like Charité Lab for Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, utilize synthetic data for clinical research. This allows data sharing and collaborative research while adhering to stringent patient data regulations.
Synthetic data stands as a multifaceted solution that bridges the divide between data utility and privacy preservation. The real-world applications, across a myriad of industries, underscore its transformative potential. Synthetic data empowers organizations to innovate, train advanced AI models, and perform data-driven analysis without compromising privacy or data security. The myriad facets of synthetic data are instrumental in addressing the complexities of data-related challenges and illuminating new horizons for business and research.