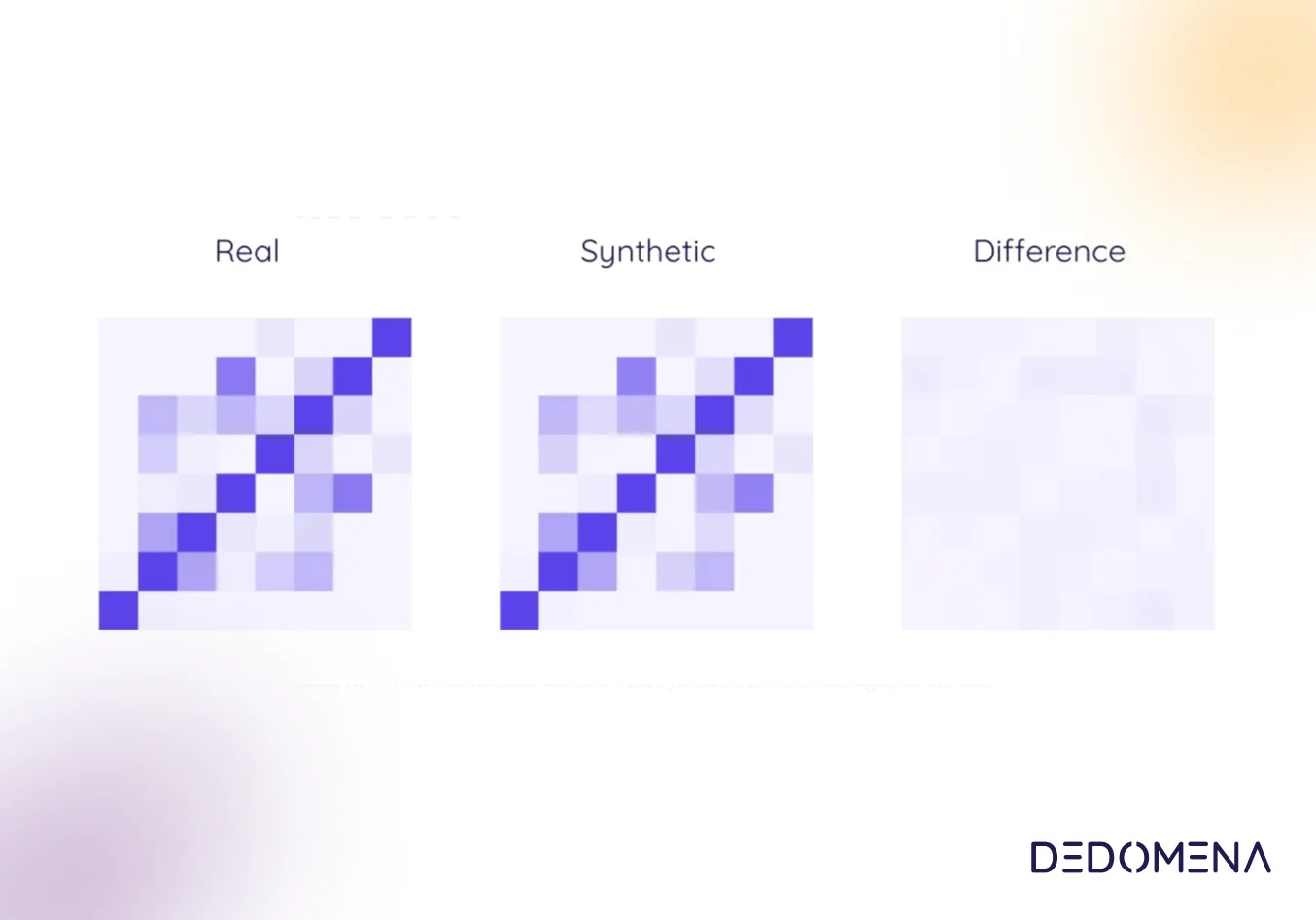
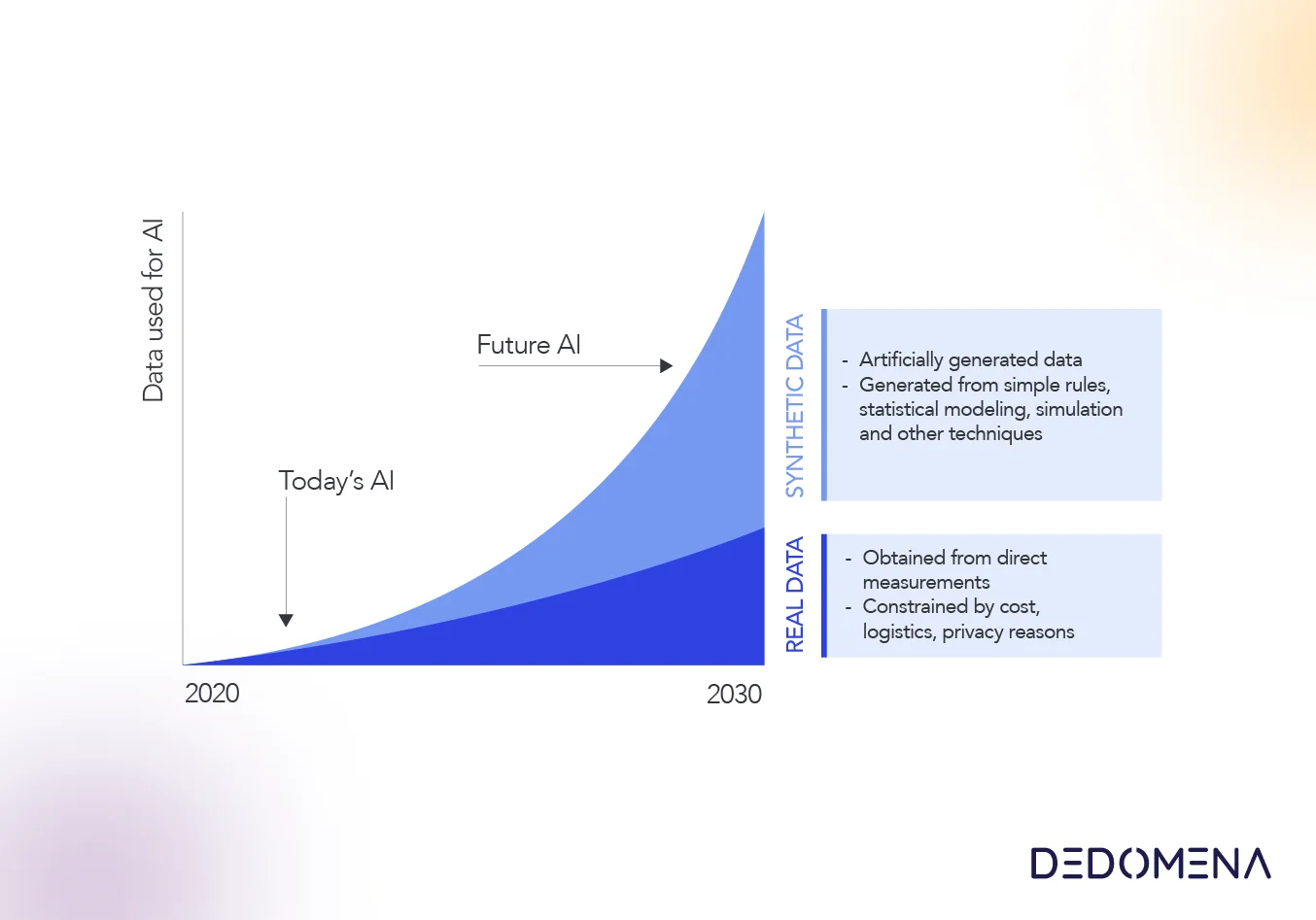
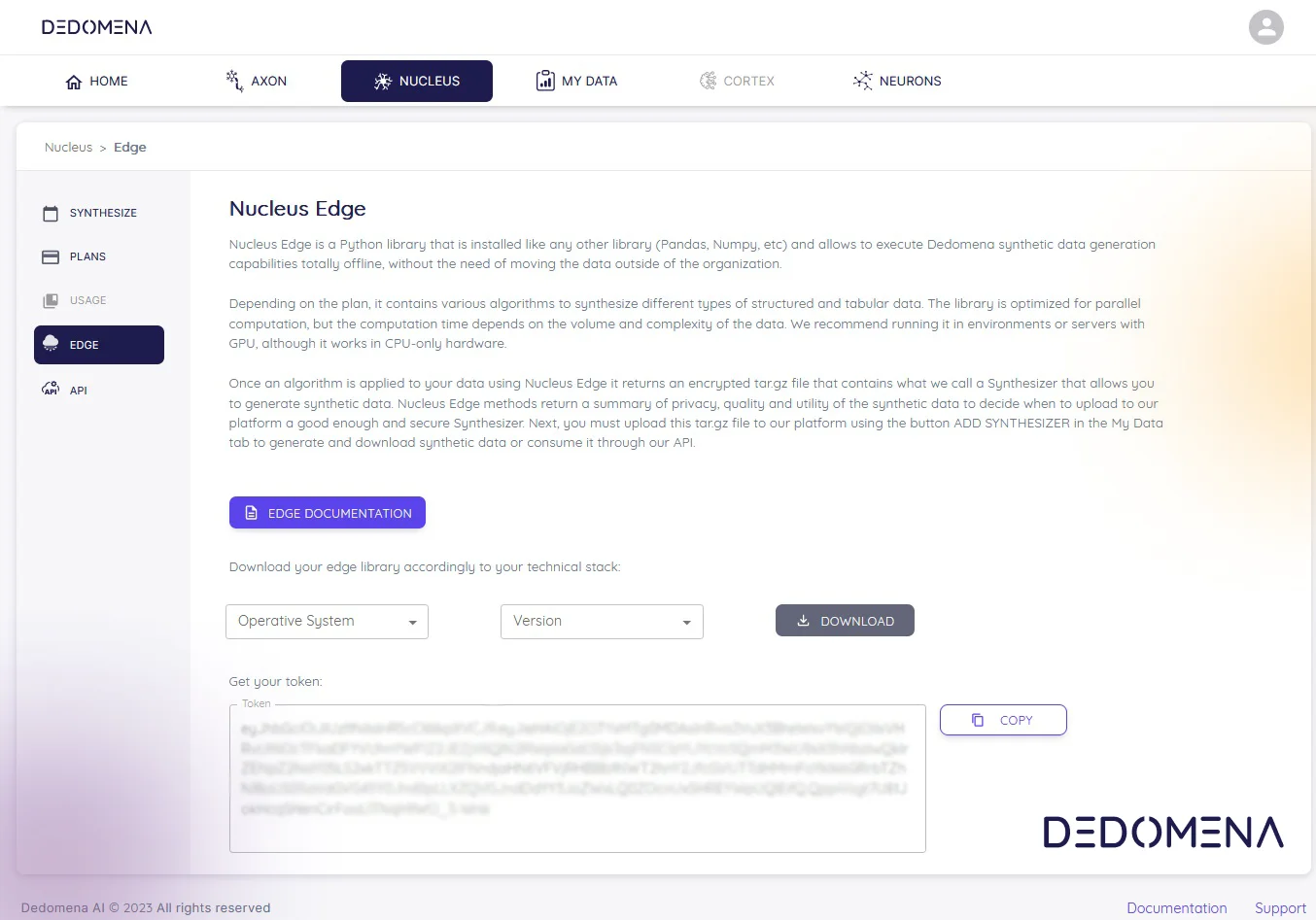
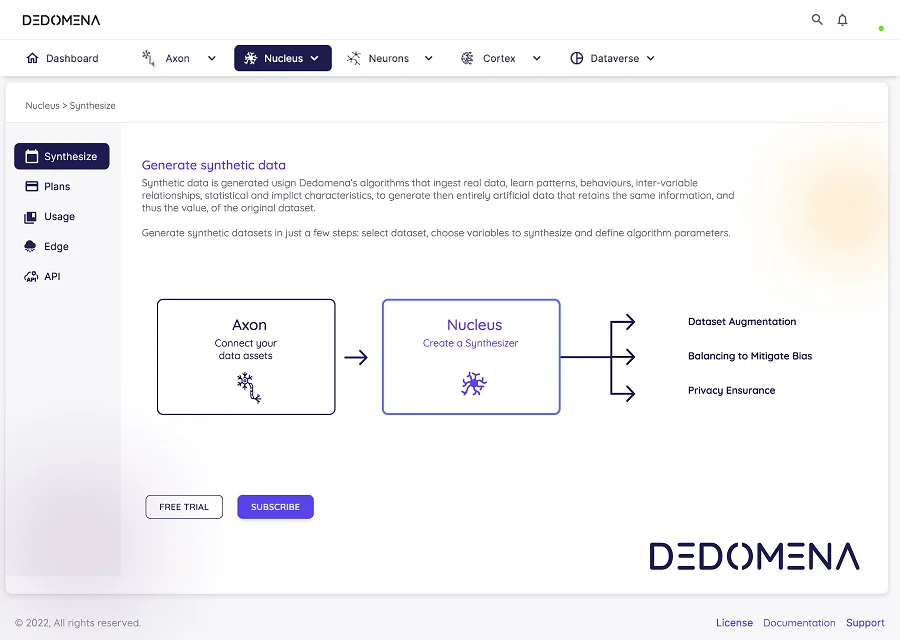
In our increasingly data-driven world, the paramount concern is privacy. As the necessity to share and analyze information for innovation grows, innovative approaches have emerged, with synthetic data standing out as a prominent solution. In this article, we'll delve into ten compelling use cases where synthetic data has proven to be an invaluable tool, unlocking the potential of data without compromising individual privacy.
1. Healthcare Research and Analysis
The healthcare industry, known for the complexity and sensitivity of its data, relies heavily on accessing and processing information. The sensitive nature of health data, including details of individuals' illnesses and medical history, requires special care. Synthetic data provides a solution by generating fictitious yet realistic patient records and medical imaging that are entirely non-identifiable. This enables medical researchers to analyze trends, test hypotheses, and develop new treatments without exposing sensitive health information.
2. Financial Services and Banking
The financial industry is undergoing a significant transformation through digitalization. Synthetic data plays a crucial role in addressing essential issues such as risk modeling, fraud detection, and market analysis. Leveraging data in financial services offers advantages like enhanced customer insights and personalized services. Synthetic data not only helps in addressing biases in datasets but also ensures compliance with data protection regulations by simulating various scenarios without using real customer data.
3. Training Machine Learning Models
As digital transformation becomes increasingly crucial in the financial sector, synthetic data continues to be a cornerstone. From addressing bias in datasets to enhancing customer insights, synthetic data contributes to more robust business dynamics and opens up new market opportunities. Privacy-preserving synthetic data allows financial institutions to simulate various scenarios without compromising individual privacy, ensuring confidentiality and compliance with data protection regulations.
4. Cybersecurity Training
Synthetic data finds application in training cybersecurity professionals by simulating cyber threats in a controlled environment. This provides a risk-free learning environment for cybersecurity teams, allowing them to hone their skills, identify vulnerabilities, and practice response strategies without exposing actual sensitive information. This is particularly crucial for industries subject to strict data protection regulations, as synthetic data mitigates compliance risks associated with exposing real and sensitive information during training exercises.
5. Human Resources and Employee Analytics
Within the realm of People Analytics, synthetic data presents a valuable solution for organizational leaders. By leveraging data to inform decisions related to the workforce, People Analytics involves collecting diverse employee data and subjecting it to thorough analysis. However, navigating the requirements of regulations such as GDPR can be challenging. Synthetic data emerges as an optimal solution, avoiding direct correlations with original records and offering a viable avenue for HR departments to innovate with new data and AI-driven technologies without compromising individual privacy.
6. Smart Cities Planning
The planning of smart cities faces the challenge of balancing innovation with individual privacy protection. Synthetic data proves to be a strategic solution, eliminating the risk of compromising the privacy of city residents. By being generated in a way that does not trace back to real individuals, synthetic data empowers urban planners to simulate and analyze diverse datasets crucial for informed decision-making. This innovative approach is pivotal in creating sustainable and efficient urban environments.
7. Marketing Analytics
For decades, studying behavior, preferences, usage, and lifestyle patterns has been crucial in marketing. Marketers and advertisers rely on research for segmentation and personalization strategies. Synthetic data elevates marketing analytics by allowing marketers to delve into the intricacies of customer behavior, preferences, and emerging trends without directly tapping into real user data. This not only safeguards individual privacy but also ensures strict adherence to privacy regulations, including GDPR.
8. Educational Research
The utility of privacy-preserving synthetic data in educational research extends far beyond its conventional applications. By providing a secure and confidential environment, researchers can explore the intricacies of educational dynamics without relying on actual student information. Educational programs can be enhanced and refined using synthetic data, allowing researchers to identify areas for improvement in curricula, teaching practices, and support systems without compromising the confidentiality of individual students.
9. Insurance
The insurance industry, undergoing significant transformation driven by insurtech start-ups and innovative, AI-powered services, relies heavily on data. Given the strategic nature of the insurance business, companies operate under highly stringent regulatory frameworks. Synthetic data generators have emerged as a solution crafted to navigate these intricate regulatory landscapes, especially concerning data-sharing limitations. Over time, synthetic data generators have evolved into robust privacy-enhancing technologies, aligning with the industry's broader shift towards innovative, technology-driven solutions that enhance both privacy and data accessibility.
10. Mobility
Vehicles serve as prolific data sources, generating vast amounts of information that fuels the development and implementation of cutting-edge applications. However, this wealth of data brings forth a significant challenge – the imperative to safeguard user privacy. Synthetic data can be used to simulate realistic traffic patterns in urban areas, crucial for city planners and transportation authorities to optimize road networks and plan for infrastructure improvements. Companies offering ride-sharing services can use synthetic data to optimize their algorithms for matching drivers and passengers, estimating demand, and improving overall service efficiency while protecting the privacy of both drivers and passengers. Researchers studying human mobility patterns can leverage synthetic data to model and analyze movement behaviors without using real location data, beneficial for understanding societal mobility trends while respecting individual privacy.
In this exploration of cases for privacy-preserving synthetic data, it’s evident that this technology has become fundamental in the era of data analytics. The ability to unlock valuable insights without compromising privacy represents a significant advancement. However, the choice of robust and privacy-respecting solutions remains essential. By adopting synthetic data approaches, organizations can move towards innovation in an ethical and responsible manner, ensuring the right balance between knowledge extraction and privacy protection in today's increasingly interconnected world.